Definition: Earth Station also known as the ground station is an arrangement of various equipment on the surface or atmosphere of the earth that is used to transmit or receive signals in the form of voice, video, or data through single or multiple satellites. It is sometimes called the earth terminal and is a part of the ground segment of the satellite network.
The earth station is an earth-based terminal that can be present on a ship or an aircraft as well. The earth station is not a single equipment entity as various major elements constitute it. It is to be noted here that the design of the earth station depends on requirements as well as the quality of service.
In today’s developing world, satellite communication has emerged as a very popular technique to enable communication via satellites due to their feature and offered advantages. Basically, irrespective of the environment, satellite communication allows the data transmission and reception from any part of the earth station to any other part with quality and reliability. Due to these reasons, satellite communication has gained huge popularity.
As we have discussed recently that satellite communication allows the communication between any point of the earth station to the other point. Thus, a satellite may communicate with multiple ground stations parallelly.
We all are aware of the fact that in today’s world satellite has become a crucial element for communication. Like from any visual information transfer to any worldwide data communication, from various data services to televising of international events, everything has been made easy with the help of satellites.
However, it is also a fact that only the presence of satellites in space has not made such activities possible. This is so because when data is transmitted from an end then it requires a proper receiving unit so that it can be utilized according to the requirement. Thus, the ground segment of the satellite network is important and the earth station is a very crucial part of it.
The earth station is a crucial part of satellite communication because one earth station transmits the signal and another earth station receives it.
The three major categories in which an earth station is divided are as follows:
As we have already discussed in the beginning the earth station is not a single entity but an arrangement of various elements that combinedly operate as a single unit.
Thus, the subsystems of the earth station, in general, are as follows:

However, these are the general equipments used for the operation but are not the only ones because there are some factors on which the requirement of equipment at the earth station depends. These are as follows:
So, we can say, earth stations are designed as per the service requirement and quality of service required.
The design and layout of the earth station are not that critical but are crucial. The reason for this is that the designing must be done in a focussed way so that the station must be able to receive even very weak signals as well as process them to get the actual information. So, designing the earth station is an important considerable factor.
The whole unit of the earth station is divided into two parts, one is the RF terminal and the other is the baseband terminal. The RF terminal includes an antenna, upconverter, downconverter, high power amplifier, and low noise amplifier. While the baseband terminal includes, encoder, decoder, modulator, and demodulator. However, these two parts are separated by a sufficient distance and are connected via IF lines. The RF terminal must be present close to the antenna unit to reduce the losses and attenuation due to the transmission line that connects the antenna with the RF equipment.
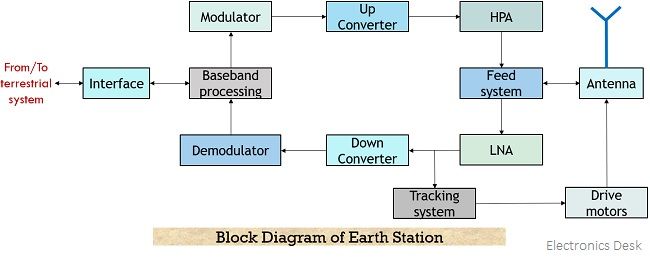
The figure below represents the block diagram representation of the transmit-receive type earth station: The fundamental operation of the earth station during transmission is to receive the signal coming from the terrestrial network and multiplex them together to link them to the satellite in order to transmit. While during the reception, it must receive the signals coming from the satellite and route it to the respective destination with the help of a terrestrial network.
Initially, the received baseband or message signal from the source is modulated with an appropriate carrier signal then it is upconverted to the desired frequency level. The achieved signal is then amplified and transmitted via antenna through feed system. However, the signal coming from the satellite is received by the receiving antenna and is provided to the feed system where required polarization is introduced. Also, the feed system maintains isolation between transmitted and received signals so as to reduce the chances of signal mixing.
So, the signal received by the feed system is fed to a low noise amplifier then is down-converted to the IF range and further demodulated and provided to the terrestrial network.
In the block diagram, we have seen units of the tracking system and drive motors. The tracking system keeps the track record of the satellite in space and is controlled by drive motors and the power supply.
The antenna unit mostly used in earth stations is reflector antenna, more specifically parabolic reflector, due to the reason that these offer high gain and low sidelobe characteristics.
It is to be noted here that with the interconnection of large traffic nodes, the designing complexity of the earth station increases. In the earth station, the G/T ratio is a crucial parameter that characterizes it. It is the ratio of antenna gain to the system noise temperature. A large earth station uses large antennas thus can manage various telephone signals and television channels. While a small earth station holds the ability to carry only one voice or TV signals.